By Jane Barthelemy.
Gluten-free is hot these days. We’d like to blame gluten for all our woes, inflammation, indigestion, headaches, and emotional blues. While it is true that gluten reactions are more common, perhaps we’re falling into wishful thinking that simply removing gluten from our diets will solve ALL our problems.In fact, there are other important triggers interact with, complicate, and exacerbate the gluten response, and these are critical for you to know.
Common mis-understandings about gluten make me wonder: What is the problem with our wheat? Is gluten the main problem? Or could it be the recent hybridization and mutagenesis of modern wheat? Perhaps the use of Monsanto’s carcinogenic herbicide Roundup Glyphosate in harvesting wheat could be causing it to be indigestible? What is the connection between gluten, high blood sugar, and the epidemic of sugar-related diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and heart disease? Is it healthy that so many commercial gluten-free products are extremely high in refined carbs and sugars? Why do doctors now say they expect people to gain weight on a gluten-free diet? Why is it that when we use time-honored traditions, like soaking, sprouting, and fermenting grains, that gluten reactions vanish and the gut can heal? How does our modern lifestyle of high-stress, multi-tasking, electronic, caffeine fueled, computerized, and Twitter-sized attention-span affect our delicate digestive system? Yep, you guessed it. Gluten is NOT the only trigger. Other important factors can cause gluten inflammation:
Top 10 Triggers for Gluten Inflammation
- Sugar: The #1 top trigger for gluten inflammation, perhaps because it is commonly eaten in combination with gluten and wheat. Sugar means any glycemic or fructose sweetener such as agave, maple, coconut, honey, rice syrup, cane, beet, refined and even unrefined sugars. That’s why I use zero-carb Just Like Sugar Table Top natural chicory root sweetener or PureLo, Lo Han Sweetener by Swanson in all my recipes. There’s no reason for weight gain on a gluten-free diet, if you cut the carbs and sugars.
- GMO ingredients in processed foods cause inflammation and bloating of the gut. GMO foods alter the gut micro-biome, damaging the immune system. To avoid GMO’s, look for 100% organic foods. Most common GMO foods are corn, soy, canola, beet sugar, zucchini, summer squash, papaya, apple, and white potato. Avoid animal products fed GMO grains by asking for grass-fed, grass-finished, organic, or wild meats.
- Toxic Glyphosate in Wheat – Spraying wheat crops with glyphosate, a Roundup product by Monsanto, just before harvest became standard practice in the late 1990’s. Interestingly, Dr. Seneff, a medical researcher at MIT discovered that when you spray the wheat plant with a toxic chemical like glyphosate, it gives higher yields as it shrivels and dies. And higher yields is an economic choice. Unfortunately most of our non-organic wheat supply is now contaminated with glyphosate. Glyphosate destroys the tiny villi in your intestines, and this in turn reduces your ability to absorb vitamins and minerals. This chart suggests a relationship between the use of toxic glyphosate, and the nearly exponential increase in celiac disease since 1990.
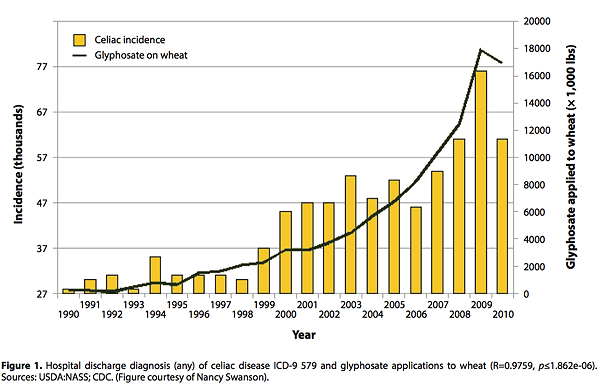 4. Refined gluten-free flours can cause inflammation, such as potato flour, tapioca flour, rice flour, corn, and oat flours. In fact, most gluten-free flours are highly processed and contain more carbohydrate content than wheat. High carbs are associated with weight gain. So there’s no reason for weight gain on a gluten-free diet, if you cut the carbs. See my article: Gluten-free Flours, Best & Worst for Weight Gain.
4. Refined gluten-free flours can cause inflammation, such as potato flour, tapioca flour, rice flour, corn, and oat flours. In fact, most gluten-free flours are highly processed and contain more carbohydrate content than wheat. High carbs are associated with weight gain. So there’s no reason for weight gain on a gluten-free diet, if you cut the carbs. See my article: Gluten-free Flours, Best & Worst for Weight Gain.
5. Mutation breeding of wheat. The semi-dwarf strain of modern wheat we now use was created by chemical mutagenesis, the purposeful induction of mutations using chemicals. The industrial compound sodium azide was used to induce mutations to the gene acetohydroxyacid synthetase to make the wheat resistant to the herbicide Beyond, or imizamox. This allows farmers to spray the herbicide freely, killing weeds (and soil micro-biome) but not the wheat.
According to Doctors Michael Antoniou, PhD, Claire Robinson, MPhil, and John Fagan, PhD, authors of GMO Myths and Truth: “Radiation-induced mutation breeding is potentially even more mutagenic than GMO [genetic modification], and at least as destructive to gene expression. Crops produced by this method should be regulated at least as strictly as GM crops.” So although wheat is not a GMO plant, it is far worse than GMO, because it has been subjected to “mutation breeding,” or mutagenesis. This is even more dangerous than GMO, because it introduces mutations not to a specific spliced gene, but throughout the entire genetic code sequences of a plant.
6. Stress, lack of sleep, depression, and hormone imbalance can trigger gluten-like reactions, especially in women during menopause. Dr. Daniel Kalish D.C states: “a strong relationship has been established in medical literature between gluten sensitivity and the hormones progesterone and estrogen. Additionally, most of my patients with gluten sensitivity have an adrenal hormone imbalance, which becomes exacerbated during menopause.” New research is pointing to gluten and food allergies as a common cause of depression and insomnia.
7. Cow dairy products and milk are common triggers for gluten inflammation, especially if raised in factory farms treated with anti-biotics, rBGH, and BHT. Now 50% of gluten intolerant people also react to dairy. Research studies throughout the world have linked milk from rBGH cows to cancer. And many countries such as New Zealand, Australia, and Japan have banned the use of BHT – Bovine Growth Hormone for cows. Even worse, most cows in the USA consume GMO grains. A solution for many people is to make the switch to organic fermented goat dairy, such as goat yogurt and kefir.
8. Coffee and caffeinated sodas can trigger an inflammation response. 10% of coffee, including decaffeinated coffee, contains a protein that triggers gluten antibodies. So if even if you’re avoiding gluten, there is a strong likelihood that the protein in your coffee could be triggering the very same gluten reactions you’re trying to avoid.
9. Nightshade vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, white potatoes, eggplant) can cause inflammation and intestinal perforations in some people which can lead to leaky gut and auto-immune diseases. Potato flour, a nightshade, is often touted as a healthy gluten-free alternative to wheat. But these nightshades vegetables are a problem for many people, and the results can be delayed weeks or months. If you’re of Caucasian descent, it’s likely that you have difficulty digesting nightshades. That’s because they are New World foods high in saponins, natural chemicals that cause perforations, or holes in the small intestine. A perforated gut is an open invitation for auto-immune diseases and food reactions. For more details see my article Beware of Nightshades.
10. Refined carbs in processed foods cause bloating and inflammation just like gluten. Swapping wheat for refined empty carbohydrates like GMO potato flour, tapioca starch, and rice flour may defeat your healthy goals. Instead try using unrefined, low-carb almond meal and shredded coconut or coconut butter. You’ll find hundreds of low-carb, GMO-free recipes on this website, and in my books Paleo Desserts and Good Morning Paleo. My yummy treats are designed to free you of addictions and avoid weight gain. We deserve delicious sweets without the health risks. Refined sugars and carbs tempt us in gluten-free aisles of every grocery. For a perfect example, check out this surprising comparison of two gluten-free brownies, one store-bought, and one from my recipes: Which Gluten-Free Brownie is Best?
Resources:
- Cross-Reaction between Gliadin and Different Food and Tissue Antigens
- Dr. William Davis, Author of Wheat Belly: Wheat is Worse Than GMO
- Three Hidden Ways Wheat Makes You Fat by Dr. Mark Hyman, MD
- Enhanced Testing for Gluten and Food Sensitivity: Aristo Vojdani, PhD
- Cascella NG, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease and gluten sensitivity in the United States, clinical antipsychotic trials of intervention effectiveness study population. Schizophr Bull. 2011 Jan;37(1):94-100. Epub 2009 Jun 3.
- Fasano A, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in at-risk and not-at-risk groups in the United States: a large multicenter study. Arch Intern Med. 2003 Feb 10;163(3):286-92.
- Sanders DS, et al. A primary care cross-sectional study of undiagnosed adult coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003 Apr;15(4):407-413.
- Hadjivassiliou M, et al. The immunology of gluten sensitivity: beyond the gut. Trends Immunol. 2004 Nov;25(11):578-582.
- Fasano A, Catassi C. Current approaches to diagnosis and treatment of celiac disease: an evolving spectrum. Gastroenterology. 2001 Feb;120(3):636-651.
- Ventura A, et.al. Duration of exposure to gluten and risk for autoimmune disorders in patients with celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1999 Aug;117(2):297-303.
- Bonamico M, et al. Tissue transglutaminase autoantibody detection in human saliva: a powerful method for celiac disease screening. J Pediatr. 2004 May;144(5):632-636.
- Ludvigsson JF, et al. The Oslo definitions for coeliac disease and related terms. Gut. 2012 Feb 16. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301346.
- Vojdani A. The characterization of the repertoire of wheat antigens and peptides involved in the humoral immune responses in patients with gluten sensitivity and Crohn’s disease. ISRN Allergy. 2011. doi:10.5402/2011/950104.
- Van den Broeck HC, et al. Presence of celiac disease epitopes in modern and old hexaploid wheat varieties: wheat breeding may have contributed to increased prevalence of celiac disease. Theor Appl Genet. 2010 Nov;121(8):1527-1539.
- Vojdani A, Tarash I. Cross-reaction between gliadin and different food and tissue antigens.
- The Root Cause of Your Autoimmune Disease — and why treating it can be easier than you think. by Dr. Jonathan V. Wright
- Celiac vs Gluten-Sensitivity vs Wheat Allergies, UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases
- Widely Used Herbicide Linked to Cancer The World Health Organization’s research arm declares glyphosate a probable carcinogen.





1 Reply to "Top 10 Triggers for Gluten Inflammation"
Angela June 7, 2024 (1:11 pm)
Thanks for this helpful info.